Sign in
New customer? Start here
Cancel
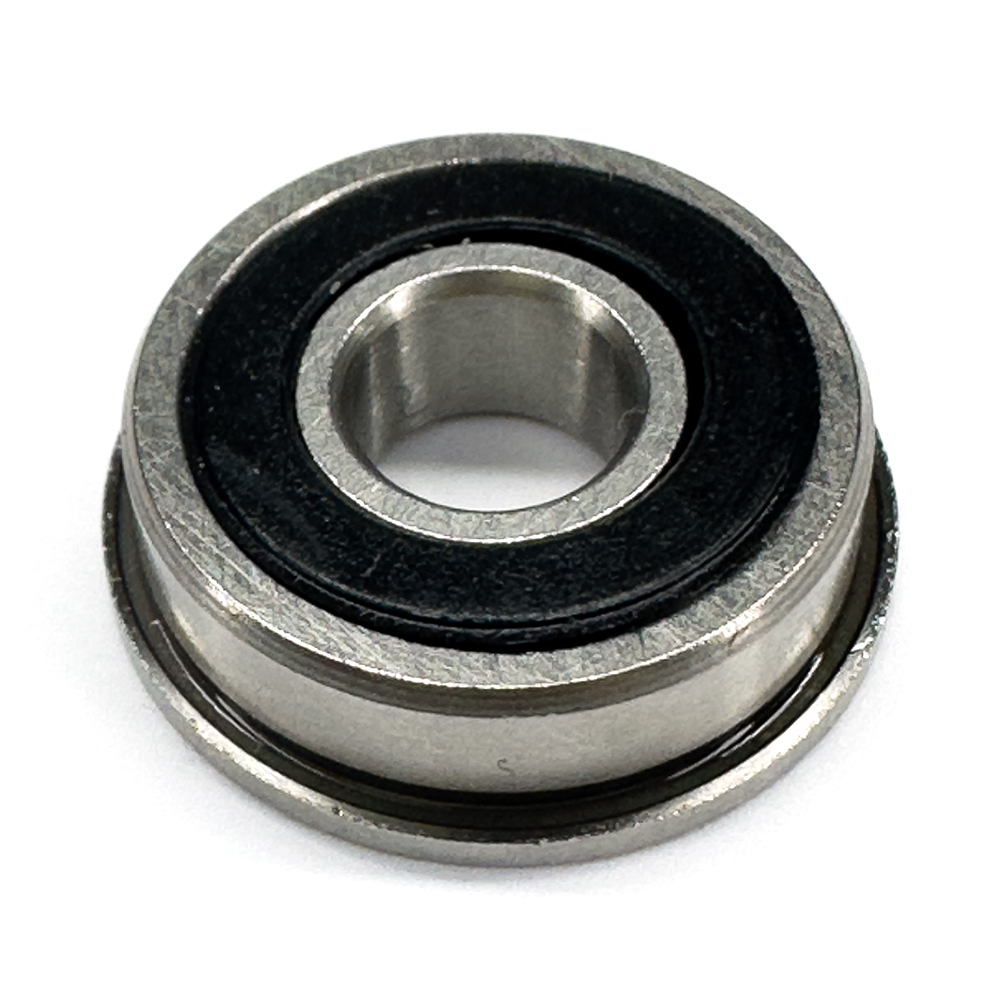
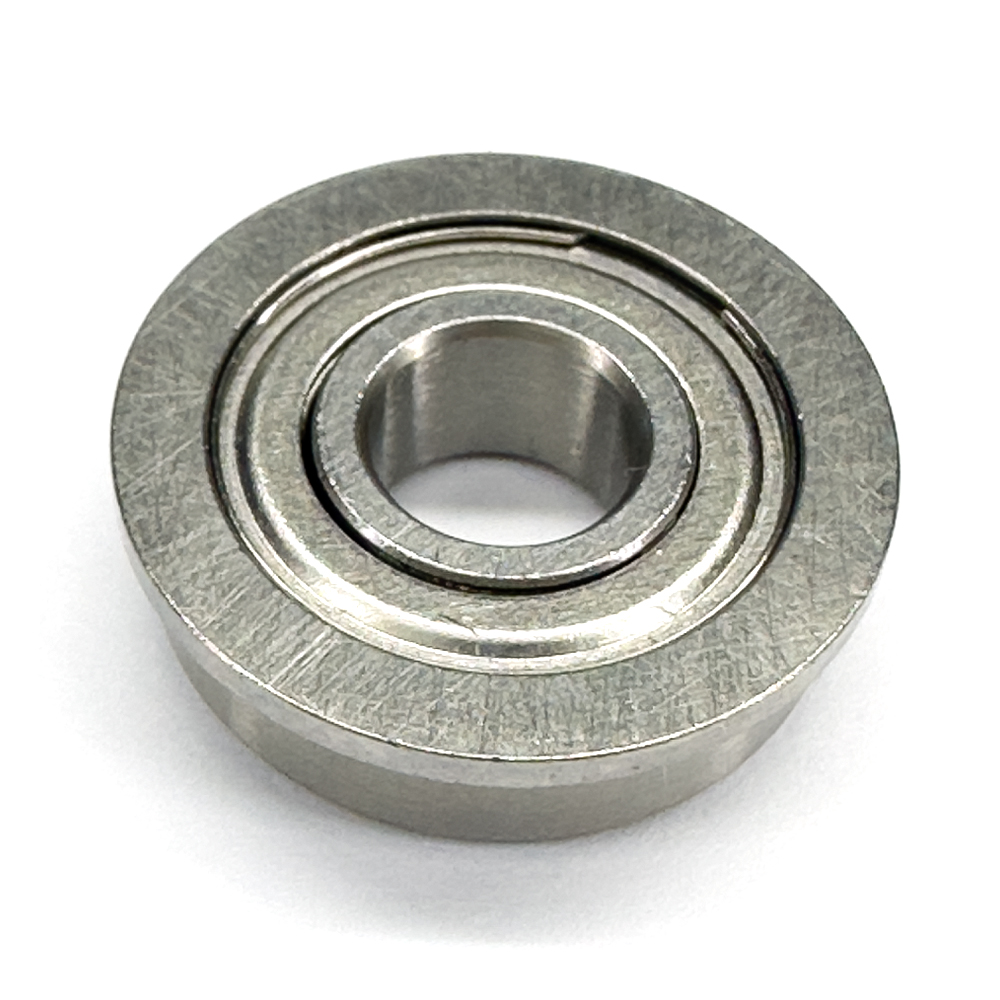
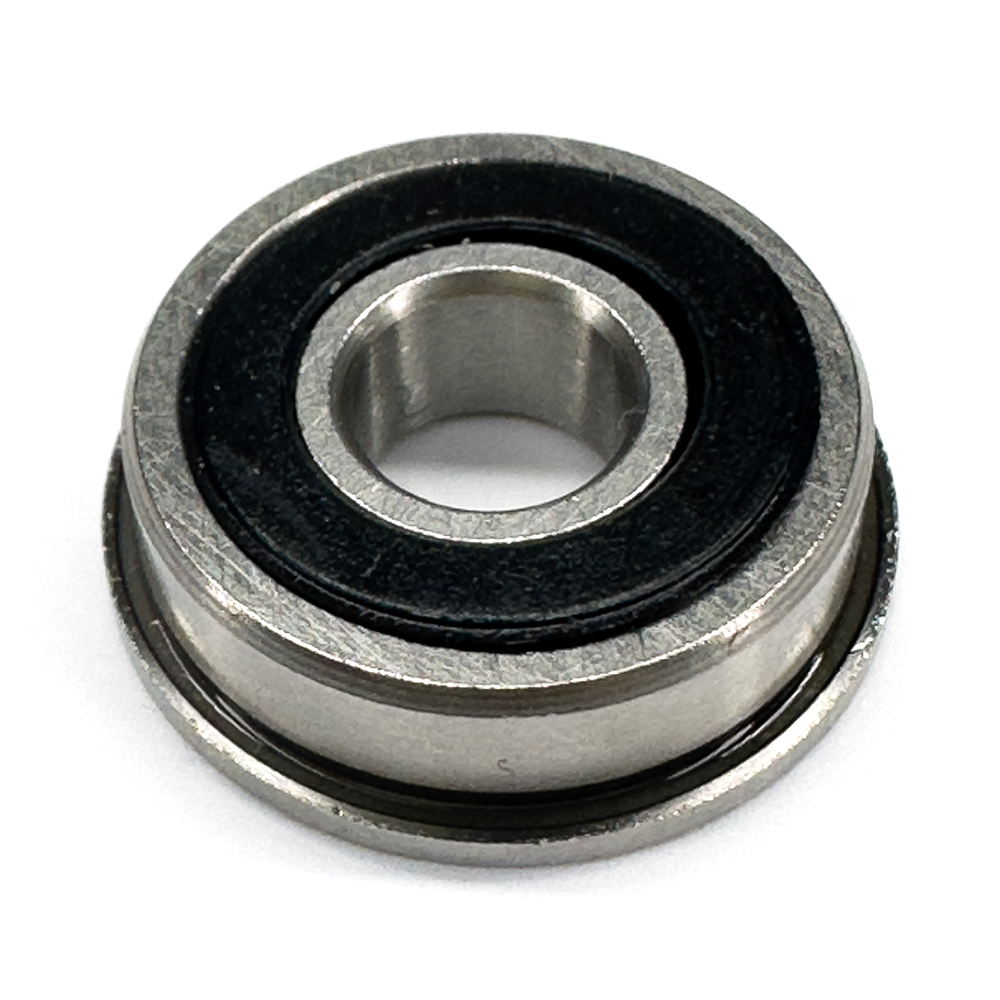
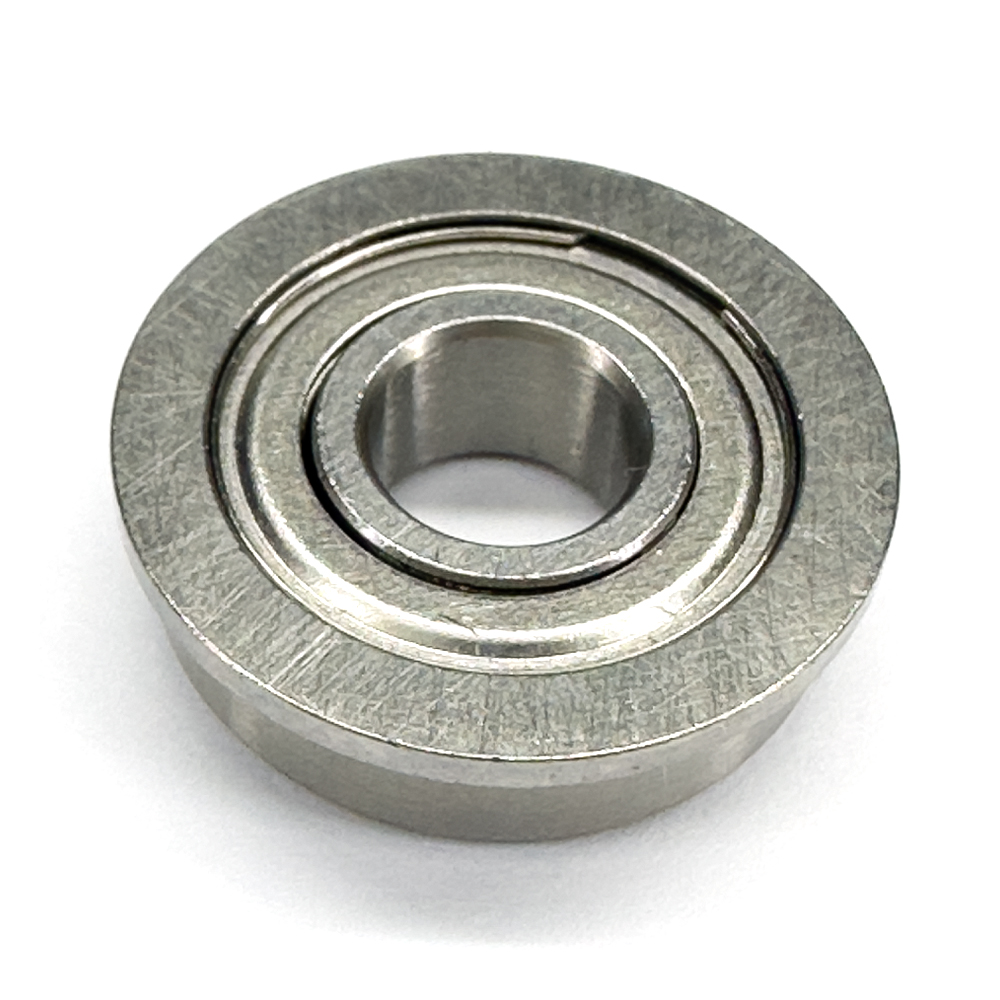
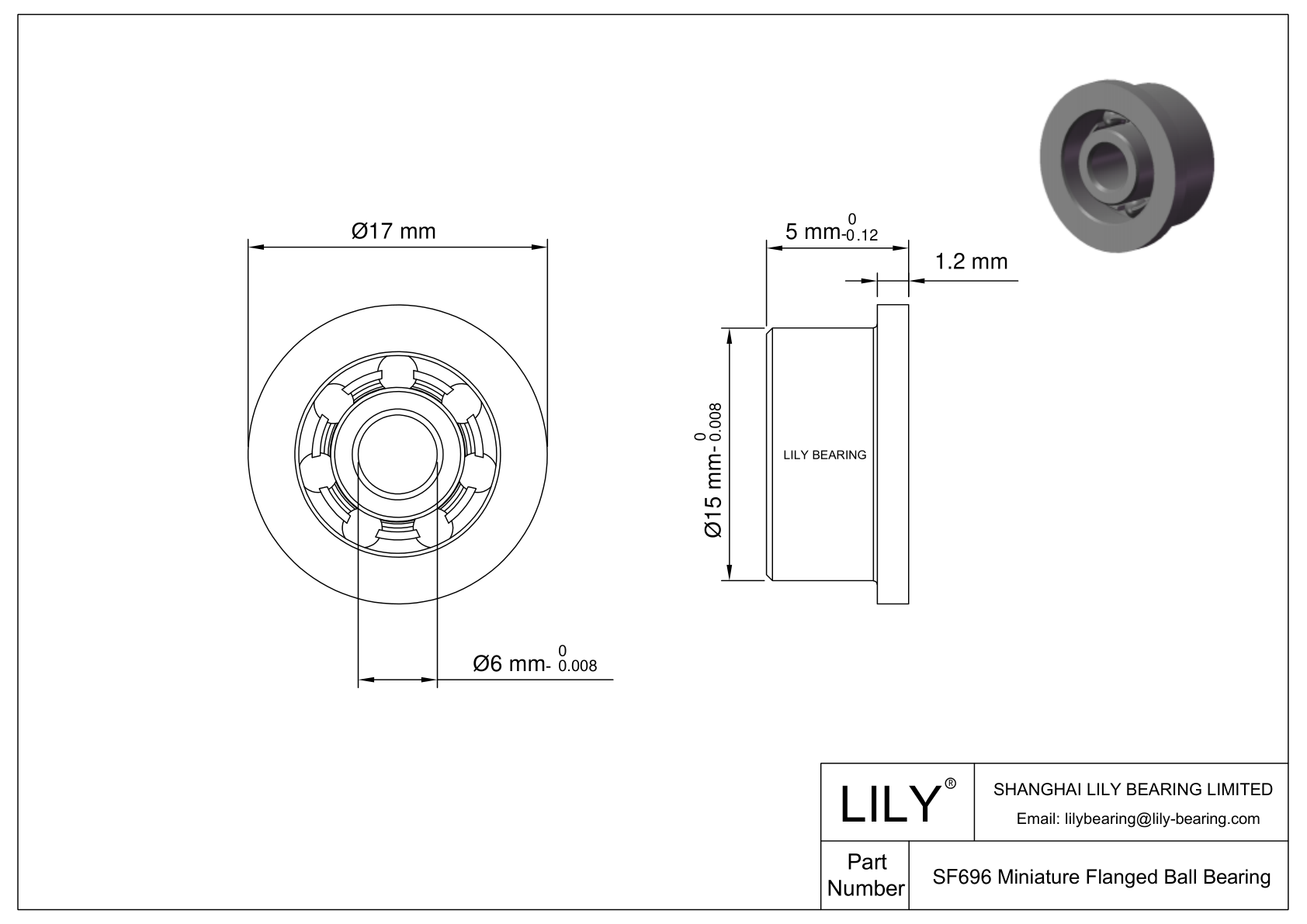
SF696

Price $ 1.62
Number
| Part Number | SF696 |
| System of Measurement | Metric |
| Bearing Type | Ball |
| For Load Direction | Radial |
| Construction | Single Row |
| Inner Ring Type | Standard |
| Seal Type | Open |
| Bore Dia | 6 mm |
| Bore Dia Tolerance | -0.008mm to 0 |
| Outer Dia | 15 mm |
| Outer Dia Tolerance | -0.008mm to 0 |
| Width | 5 mm |
| Width Tolerance | -0.12mm to 0 |
| Flange Outer Dia | 17 mm |
| Flange Thickness | 1.2 mm |
| Ring Material | Stainless Steel |
| Ball Material | Stainless Steel |
| Cage Material | Stainless Steel |
| Dynamic Radial Load | 231 lbf |
| Static Radial Load | 85 lbf |
| Max Speed (X1000 rpm) | 36 |
| Lubrication | Required |
| Shaft Mount Type | Press Fit |
| Temperature Range | -30° to 110 °C |
| ABEC Rating | ABEC1 |
| Radial Clearance Trade No | MC3 |
| Radial Clearance | 0.002mm to 0.013mm |
| RoHS | Compliant |
| REACH | Compliant |
| Ball Dia | 2.3810 mm |
| Ball Qty | 7 |
| Weight | 4.24 g |
INTERCHANGE
The LILY Bearing part series SF696 is a potential replacement for these common bearing part numbers.
LILY
NMB
DYNAROLL
EZO
NHBB
McMaster-Carr
LSF696
DDRF-1560
F696h
F696h
SSRF-1560
57155K479
Design Features of SF696 Bearing
SF696 Bearing is designed to effectively handle radial loads, provide precise alignment and facilitate easy mounting in applications where axial positioning is essential. SF696 bore dia is 6 mm. Its out dia is 15 mm. SF696 flange outer dia is 17 mm and its flange thickness is 1.2 mm. Its robust construction and flange design can offer reliable performance and extended service life.
What Benefits Can SF696 Bearing Provide?
- Precise Axial Positioning: The integrated flange aids in securing the bearing axially, ensuring optimal alignment.
- Simplified Installation: The flange allows for easier bearing assembly and disassembly, reducing maintenance time.
- Enhanced Durability: This bearing typically has robust construction for prolonged service life, even in demanding applications.
- Reduced Friction: Their design aids in lowering friction, promoting energy efficiency.
What Can SF696 Bearing Be Used for?
SF696 Bearing is suitable for a wide range of applications due to their design and load handling capabilities, including:
- Automotive: used in assemblies like transmissions, steering mechanisms, and wheel hubs
- Industrial Machinery: such as conveyor systems, electric motors, and various mechanical handling systems
- Home Appliances: such as washing machines, air conditioners, and refrigerators
- Aerospace: used in aircraft control systems and satellite equipment
- Electronics: like hard drives and DVD players
- Robotics: used in robotic arms and automated machinery