
Sign in
New customer? Start here
A Guide to Choosing Ball Bearings
Introduction to Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are parts that help things move more smoothly by reducing friction between moving parts. They have two rings (inner and outer) with balls in between that help with rotation or straight movement.
Ball bearings are important parts used in many industries, like automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and so on. Ball bearings are important for making machines work better and reducing wear. They also help parts last longer by reducing friction.
Types of Ball Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are a type of bearing designed to support both radial and axial loads.
Deep groove ball bearings are used in electric motors to reduce friction and improve efficiency. They also support moving parts in vehicle motors and are found in machinery, conveyors, and household appliances.
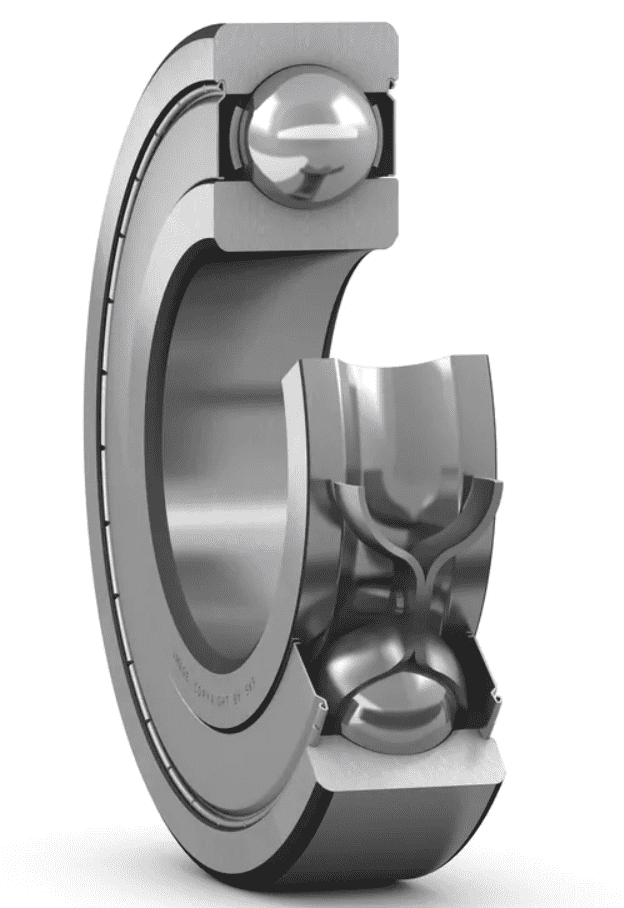
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings are made to handle both radial and axial loads. The balls are positioned at an angle to the raceways, which helps them handle forces from different directions.
Angular contact ball bearings are often used in machine tool spindles. They help with precise positioning and allow for high-speed operation. They are also found in vehicle hub bearings to ensure smooth wheel rotation and stability. Additionally, these bearings are used in pumps, where they help maintain alignment and reduce wear during operating condition.

Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust ball bearings are made to support axial loads, which are forces that push or pull along the bearing's axis. They have two rings and balls that can handle these thrust loads well, making them suitable for situations where such forces are involved.
Thrust ball bearings are often used in industrial fans to support axial loads while they run. They are also found in aerospace applications, where they help aircraft parts perform reliably. Additionally, these bearings are used in cars, such as in clutches and gear systems.
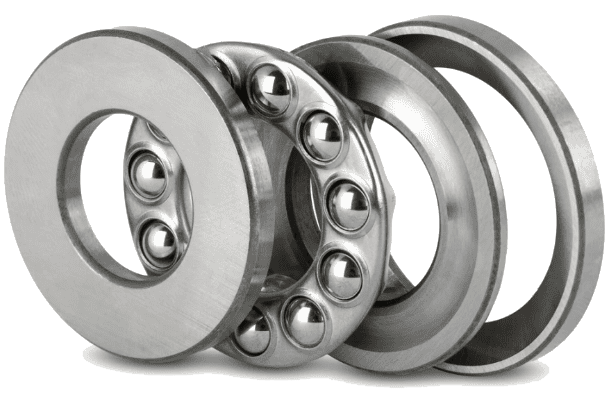
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Self-aligning ball bearings have an inner and outer ring designed with a spherical raceway. These bearings can correct misalignment and handle minor bending of the shaft. This means they can continue to function properly even if the shaft is not perfectly aligned.
Self-aligning ball bearings are ideal for use in gearboxes and long shafts in heavy machinery. Their ability to accommodate misalignment makes them well-suited for applications where shaft alignment may be an issue.
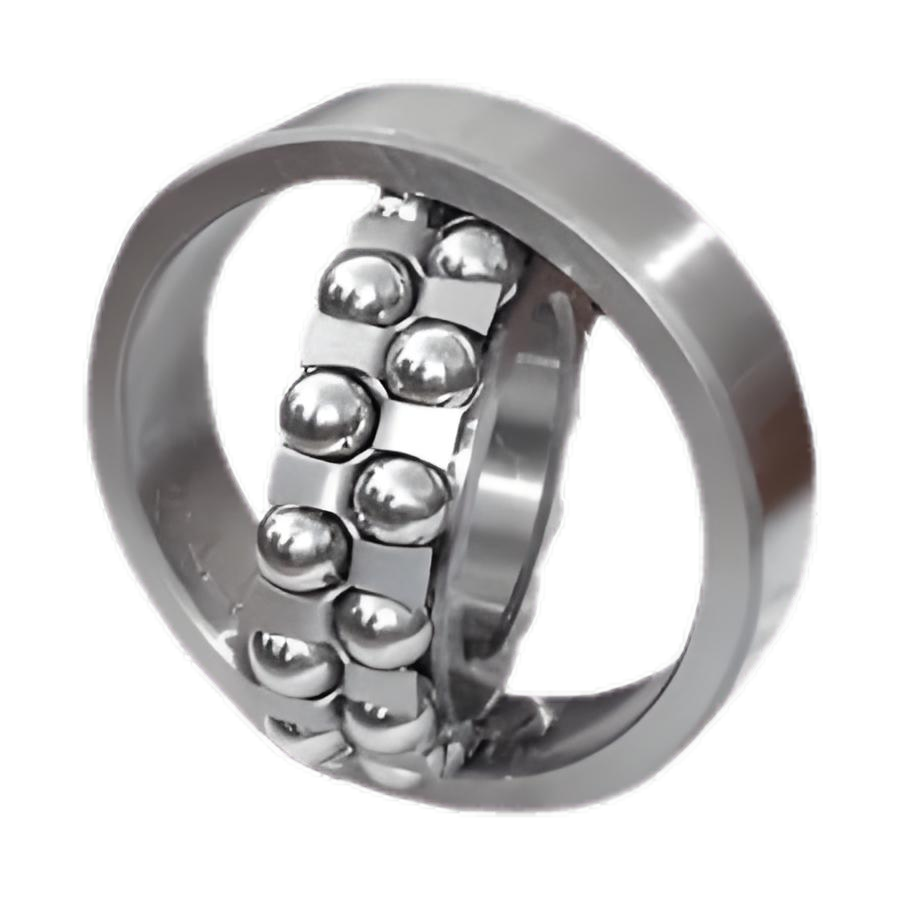

Miniature Ball Bearings
Miniature ball bearings are small bearings made for tight spaces. They offer high precision and smooth operation. These bearings are usually made from stainless steel, which is resistant to corrosion and very durable.
Miniature ball bearings are used in precision instruments like measuring devices and gyros. They are also found in flow meters, where their small size and accuracy help ensure correct readings and smooth operation.
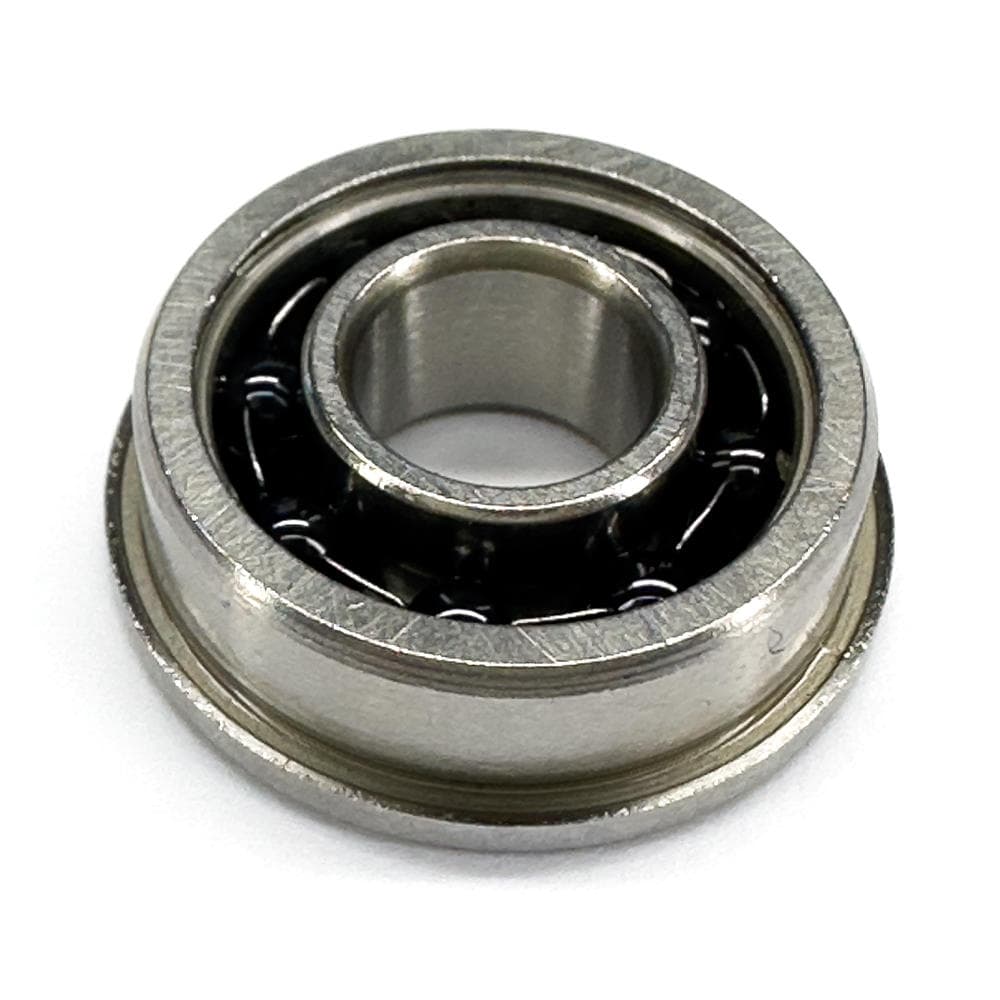

Thin Section Bearings
Thin section bearings are special bearings with a smaller size compared to regular bearings. Their lightweight and compact design reduces the weight and size of machines. This makes them ideal for tight spaces or weight-sensitive uses. Even though they are small, they can still handle high loads.
Thin section bearings are often used in aerospace for lightweight parts. They are also used in medical devices where accuracy and small size are important. Additionally, these bearings help robotics move smoothly in tight spaces.
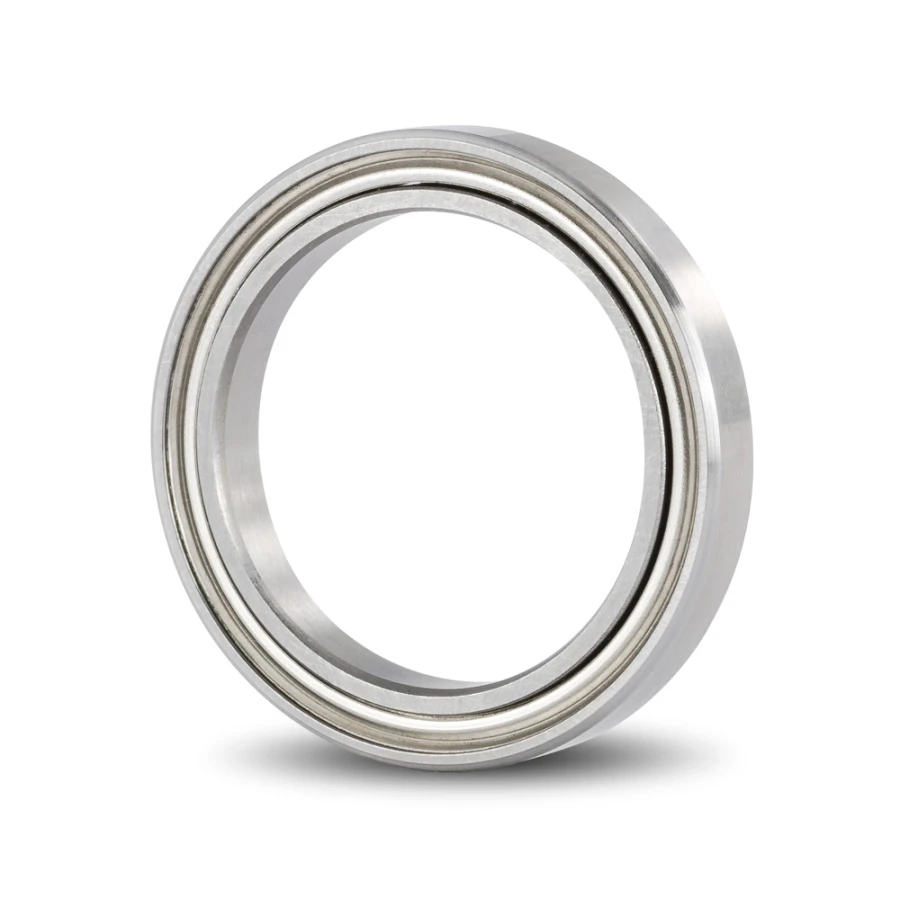

Flanged Ball Bearings
Flanged ball bearings have a flange on the outer ring that keeps the bearing secure. This flange provides stability during operation, preventing the bearing from shifting. It also allows for easy mounting and precise positioning in its housing.
Flanged ball bearings are commonly used in cars, industrial machines, and electric motors. They offer reliable performance and are easy to install.
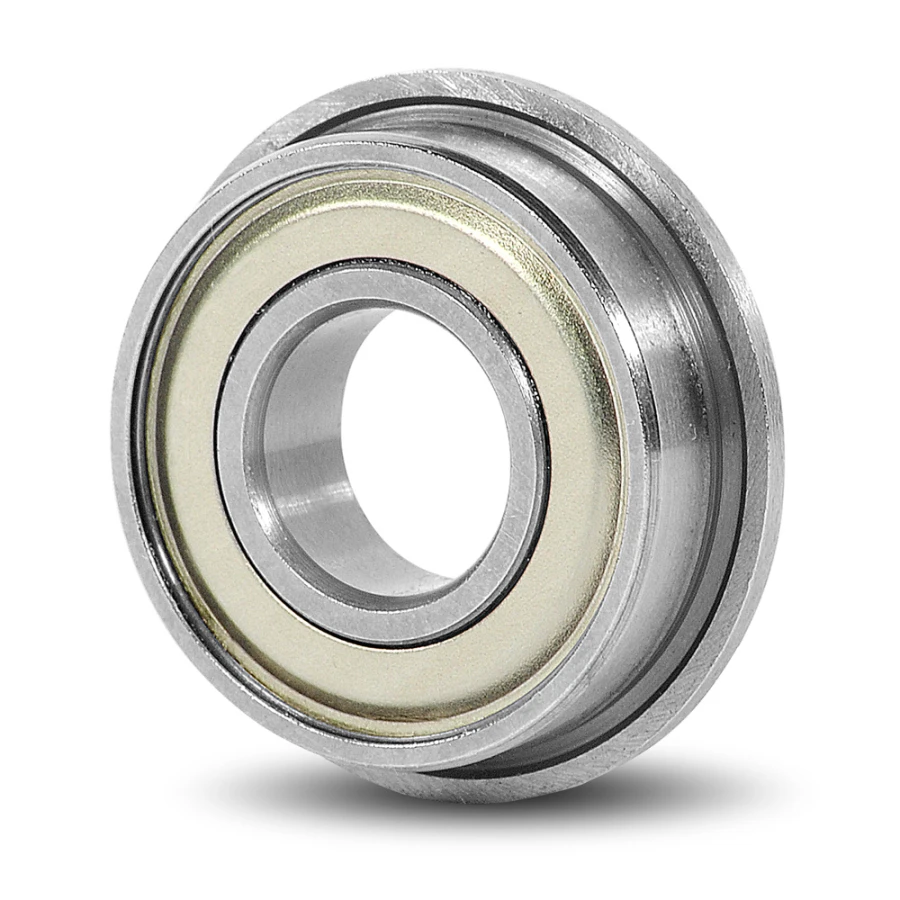

Mast Guide Bearings
Mast guide bearings are special bearings that support the movement of masts in different machines. They help ensure smooth operation by guiding the mast as it moves up and down. These bearings can support heavy loads and occasional thrusts. This makes them strong for tough jobs and keeps stability during use.
Mast guide bearings are often used in material handling equipment like forklifts to support the lifting mechanism. They are also found in automated machines to ensure smooth movement and improve efficiency.

Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Ball Bearings
Load Type and Capacity
Radial loads are forces that act vertical to the axis of the bearing. Axial loads are forces that act along the axis. Understanding these load types is essential for selecting the right bearing for a specific application.
The type and size of the load play a crucial role in choosing the right bearing. Picking a bearing that can handle the expected loads helps it work well and last longer.
Choose the right bearing for the type of load—radial, axial, or combined—to ensure it works well and lasts longer. Choosing the right bearing ensures efficient operation and lowers the chance of machinery failure.
Speed Requirements
Bearings are made for different speeds, and picking the right one depends on how fast the application moves. High-speed applications need bearings that can handle quick movements. Low-speed applications focus more on durability and load capacity.
Speed has a big impact on how bearings are designed and perform. High-speed bearings are usually made with lighter materials, special lubricants, and tighter fits to reduce friction and heat. On the other hand, low-speed bearings are often built to handle heavier loads and don’t need as much focus on heat.
When choosing bearings for high-speed applications, make sure to select those designed for this purpose. Look for bearings that have low friction, higher speed ratings, and the right lubrication. Also, consider factors like temperature resistance and material quality to ensure they work well and last long.
Bearing Material
The most common materials for bearings are stainless steel, ceramic, and chrome steel. Several factors influence the choice of bearing material. These factors include load capacity, rotation speed, temperature, and resistance to corrosion.
Different industries have specific needs for bearing materials. In the medical industry, bearings should be made from safe materials that can be easily sterilized. In food processing, they need to resist corrosion and be easy to clean for hygiene.
Sealing and Lubrication
Choosing the right sealing system for bearings is important for how well they work and how long they last. Shielded, sealed, and open bearings provide different levels of protection against dust, dirt, and moisture.
Grease and oil are two main types of lubricants for bearings. Grease creates a thicker layer of protection against dirt, while oil helps to keep the bearings cool. Choosing the right lubricant is important because it affects how long the bearings last and how well they perform.
To make ball bearings last longer, regular maintenance is key. This means checking and adding lubricant, looking at seals for wear, and keeping the bearings clean.
Ball Bearing Applications Across Industries
Automotive and Aerospace
Ball bearings are widely used in cars, especially in transmissions, wheels, and gearboxes. They help ensure smooth movement and reliable performance in these important parts.
Using ball bearings greatly improves performance, durability, and efficiency. They reduce friction and wear, which helps vehicles run better, last longer, and use less fuel. This makes them essential in today's automotive and aerospace designs.
Manufacturing and Heavy Machinery
Ball bearings are important in manufacturing equipment because they reduce friction. This helps machines run smoothly and efficiently, boosting productivity.
Ball bearings are often used in manufacturing applications like conveyors, cooling fans, and motors. They ensure these machines operate reliably and perform better.
Medical and Precision Instruments
Ball bearings are vital for high-precision applications like imaging devices, gyros, and robotic systems. They ensure accurate movement and reliable performance in these sensitive tools.
In sensitive environments, the material and design of bearings are important. They need to be made from safe, strong materials that can handle sterilization and keep their precision.
How to Maintain Ball Bearings for Optimal Performance
Regularly inspect ball bearings for dirt, debris, or signs of pollution. Clean them using appropriate solvents and tools to prevent buildup that can affect performance.
Monitor for unusual sounds or vibrations during operation, as these can indicate wear or damage. Early detection helps prevent major failures.
Follow manufacturer guidelines for re-lubrication intervals. Use high-quality lubricants and apply them correctly. This can minimize friction and extend bearing service life.
Conclusion
Choose bearings based on the specific application, ensuring they meet the required load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions. Selecting the correct bearing ensures longer service life, reduces downtime, and improves overall performance.
Consider the material's resistance to corrosion and wear when selecting bearings. Make sure the bearing has enough load capacity and can handle the operating speed for optimal efficiency.
Keep Learning







