What Is a One Way Bearing?
One way bearing plays a crucial role in various industry. It is a type of bearing that allows rotation in one direction while locking the bearing in the opposite direction to transmit torque. Its unique design and functionality make it indispensable in various mechanical systems. This blog will explore what a one way bearing is, its design, functions, applications, benefits, and significance in various industries.
Understanding a One Way Bearing
A one way bearing is a type of needle roller bearing constructed from a drawn cup with needle roller clutches, which have a small radial section height.
These one way needle bearings permit rotational movement in one direction while preventing motion in the opposite direction. This is achieved through a mechanism that allows the needles to roll freely in one direction but lock when the rotation reverses, thus transmitting torque efficiently.

Other Names of a One Way Bearing
One way bearing also has other names, such as:
- 1 way bearing
- one way clutch
- one way clutch bearing
- sprag clutch bearing
- one way sprag clutch
- one way roller clutch
- one way needle bearing
- one way needle roller bearing
Design and Construction
Needle Roller Clutches
Needle roller clutches are mechanical components used in machinery to allow the rotation of shafts in one direction while preventing rotation in the opposite direction. A one way bearing is compact, lightweight, and operates directly on a shaft.
The miniature one way clutch consists of a drawn cup, rollers, cage, and springs. The drawn cup, made of carburized steel sheet, has a unique structure with a protruding portion that serves as a stopper of rotation on the outside surface at the O.D. side, and a cam on the outer ring at the bore side.
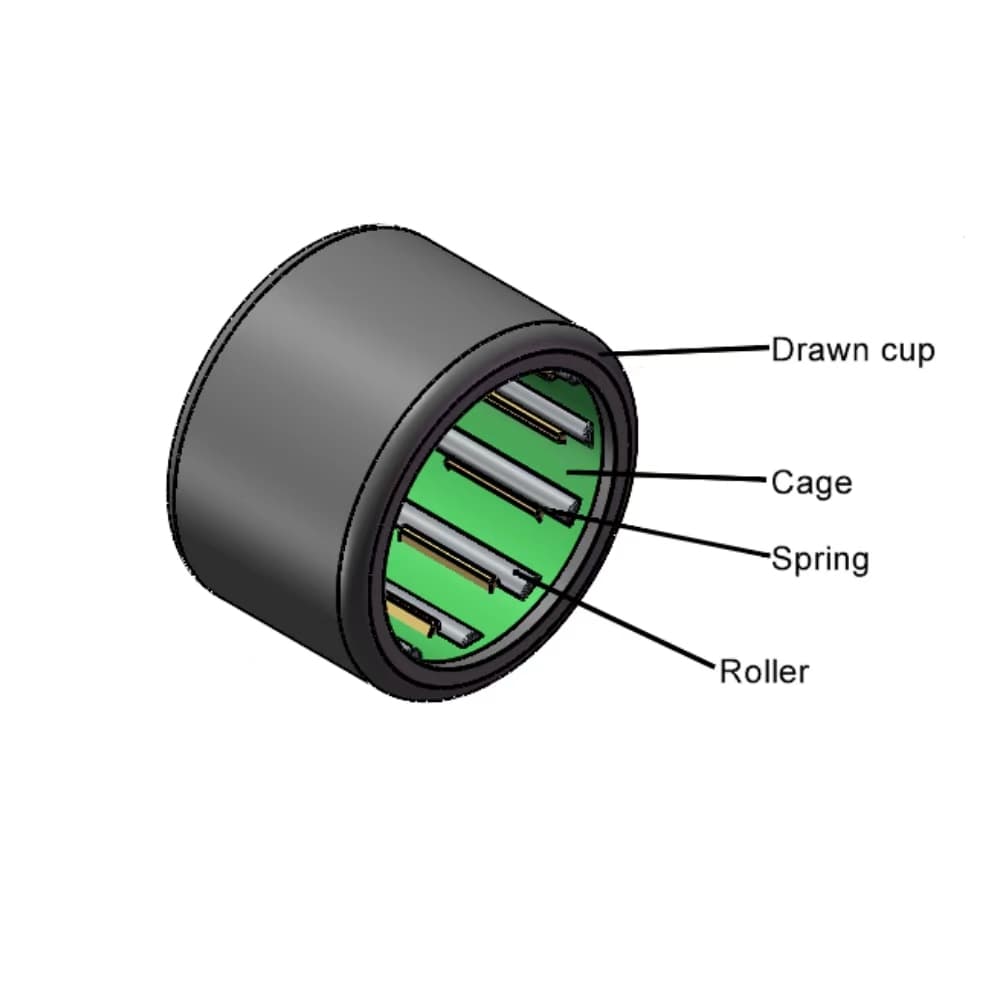
Needle roller clutches serve as critical components in one way bearing by enabling the following functionalities:
- Unidirectional Rotation: It allows shafts to rotate freely in one direction while locking and preventing reverse rotation.
- Torque Transmission: Efficiently transmit torque when engaged, providing high load-carrying capacity due to the line contact of needle rollers.
- Overrunning: It allows the outer race to overrun the inner race without transmitting torque, useful in applications requiring differential speeds.
Single-Row and Triple-Row Bearings
- Single-Row Bearings: These one way bearings do not support loads from any direction and should be used with needle-roller bearings to support radial loads.
- Triple-Row Bearings: These support radial loads, making them more versatile for applications that require both one-way locking and load-bearing capabilities.
Materials Used
Common materials used in one way bearing include:
- Stainless Steel: It can provide excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making it a common choice for various bearing components.
- Carburized Steel: It undergoes a heat treatment process to enhance hardness and wear resistance, suitable for raceways and rolling elements.
- Plastic Springs: It can be used for lightweight and low-friction applications, reducing the overall weight of the bearing and ensuring smooth operation.
How One Way Bearing Works
One way bearing allows rotation in one direction while preventing it in the opposite direction.
Mechanism of Action
Their operational mechanism involves several key components and principles:
- Inner and Outer Races: These are the two primary rings of the bearing. The inner race is typically attached to a rotating shaft, while the outer race is fixed to the housing or vice versa.
- Rolling Elements: Depending on the design, these can be rollers, sprags, or cams. They are positioned between the inner and outer races and are responsible for the locking and freewheeling actions.
- Sprags/Rollers: These elements are designed to engage and lock in one direction of rotation. When the inner race rotates in the desired direction, the sprags or rollers tilt slightly and create a wedging effect, locking the inner and outer races together. This enables torque transmission.
- Retainer/Spring Mechanism: A retainer or spring mechanism keeps the sprags or rollers properly aligned and maintains their position relative to the inner and outer races.
- Freewheeling Direction: When the inner race rotates in the opposite direction, the sprags or rollers disengage due to their specific geometry or the action of the retainer spring. This allows the inner race to rotate freely without transmitting torque to the outer race.
Free Motion vs. Locking Motion
The difference between a one way bearing's free motion and locking motion lies in the direction of rotation and the corresponding behavior of its internal components.
- Free motion refers to the condition where the bearing allows rotation without transmitting torque, effectively disengaging the connection between the inner and outer races. It commonly used in when rotation is needed without driving the load.
- Locking motion refers to the condition where the bearing engages and transmits torque, effectively locking the inner and outer races together to rotate as one unit. It is commonly used in when rotation must drive the load or machinery.
Advantages of A One Way Bearing
- High Torque Transmission: Capable of transmitting high torque efficiently.
- Minimal Backlash: Transition from free motion to lock occurs with minimal backlash, ensuring smooth operation.
- Durability: It is designed to operate in a wide temperature range, providing long-lasting performance.
Applications of A One Way Bearing
One way bearing is used in various industries due to its reliability and efficiency. Common applications include:
- Office Equipment: Paper movement in copiers, fax machines, and paper towel dispensers.
- Fitness Equipment: Ensuring smooth operation in exercise machines.
- Automotive Industry: It can be utilized in two-speed gearboxes and rack indexing drives.
- Recreational Gear: It is found in fishing reels, RC cars, RC helicopters, and RC engines.
Installation and Maintenance
- Proper Mounting: One way needle roller bearing is easily mounted with a simple press fit in the housing. Proper mounting ensures the final dimension and geometric accuracy of the outer ring, which is crucial for optimal performance.
- Maintenance Tips: Regular maintenance of one-way bearing involves inspection, proper lubrication, cleanliness, correct handling and installation, monitoring operational conditions, managing loads, timely replacement of worn components, and keeping detailed maintenance records.
Special Notes and Considerations
- Temperature Range: For environments above 70°C, oil lubrication is recommended to maintain the efficiency and longevity of the bearing. One way needle bearing assemblies can typically operate within a temperature range of -30°C to 120°C.
- Customization Options: We offer custom solutions to fit your specific needs. Our one way bearings can be tailored to ensure optimal performance in your unique conditions. For example, we can use stainless steel for enhanced durability and corrosion resistance.
Conclusion
One way bearing is essential for numerous mechanical systems due to its unique ability to allow rotation in one direction while locking in the opposite direction. It can ensure efficient torque transmission and minimal backlash. Whether used in office equipment, automotive systems, or recreational gear, one way bearing offers reliability, high torque transmission, and ease of maintenance.
For top-quality one way bearing and expert guidance, trust LILY Bearing to provide the best solutions for your needs. Explore our extensive range of bearings and enhance the performance and longevity of your machinery.
Keep Learning








